Penetration Testing
Put your security system to test today
Securing an organization’s systems, data, networks, and other valuable assets is an ongoing process. None of your security strategies and best practices are ever enough to build a concrete wall between you and intruders. However, there’s one way to keep them away. Finding the existing and potential cyber vulnerabilities before perpetrators do would help you in the long run. Penetration testing is one such process that enables you to identify the loopholes and weaknesses of your system. It gives you enough time to patch the vulnerabilities before anyone can use them to your disadvantage.
What Is Meant by Penetration Testing?
The advancement of technologies and rise in cyber-attacks, have led organizations to think and focus more on their IT infrastructure. It has become a cause of concern for organizations because every vulnerable area present in the applications may provide hackers with an opportunity to exploit it.
Penetration testing is also called a pen test; It is a testing method to reveal vulnerable areas present in the system. Weak vulnerabilities found are the critical passage to malicious activities and unauthorized access to exploit any computer system.

To protect your networks against such malicious attacks, organizations need to take advantage of professional expertise to secure their infrastructure and applications. A pen tester is hired to conduct and identify such security loopholes and ensure the protection of sensitive data. Usually, organizations perform pen-testing only when there is a significant setback, or their product needs an upgrade. However, it should be considered a standard and a recurring process within the organization’s IT security roadmap.
Role of a Pen Tester
By now, we have understood what pen testing is. To move further, we need to understand who will perform a rigorous security check of an organization’s IT profile and the role of the professional in this task. A pen tester is hired to find out the loopholes in a company’s IT infrastructure. The process starts with evaluations, analysis, internal and external assessments, looking for vulnerabilities, etc. Below are the actions the tester performs during the pen testing process:
- Perform tests to identify weaknesses across systems and networks
- The pen tester has complete access to a component of the system (which includes confidential data and information).
- Testing of internal security systems.
- Pinpoint exposures to protect sensitive data.
- Review current policies and procedures and redefine them for better security standards.
- Enhance current security posture and suggest implementing robust security standards
- Security awareness and education
- A pen tester should provide a detailed report containing all information about the vulnerabilities, their details, and other related information in a precise and effective manner to the senior management.
What Are the Types of
Penetration Testing?
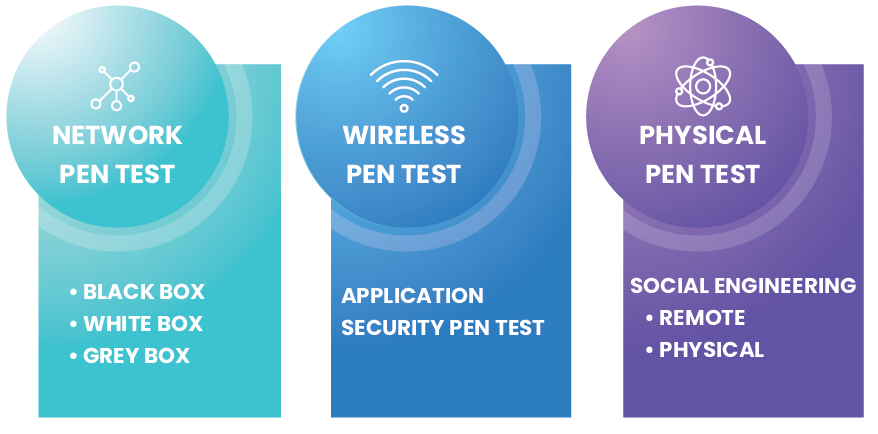
Network Pen Test
In black-box engagement, the tester does not have access to any of the client’s internal network. He only collects information about the target network or system and does not examine any programming codes. In this type, the tester need not be an expert because the nature of the job does not demand any specific language knowledge.
In this category, the tester has complete access to the applications and systems. For example, source code, OS details, IP address. This type is also known as structural, glass box, clear box, and open box testing. The goal of the white box phase is to identify deficiencies in areas such as security exposures, security misconfiguration, poorly written development code, and lack-of-defensive measures. This assessment is more comprehensive, as both internal and external vulnerabilities are tested.
In this type, the tester has internal access and knowledge that may come in the form of lower-level credentials, application logic, flowcharts, or network infrastructure maps.
Wireless Pen Test
Wireless applications and services are targeted in this test, including routers, filtering packets, encryption, and decryption. Just as wired networks are pen tested, wireless interfaces also need to be tested. Wireless networks are always risky because of their remote operations. Potential attackers can hack wireless networks from anywhere, so it is critical to assess and secure wireless networks. A wireless penetration test is an authorized hacking attempt designed to detect and exploit vulnerabilities in security controls used by several wireless technologies, misconfigured access points, and weak security protocols.
Social Engineering Test
This is the most popular and secure method to extract confidential information and sensitive data via the internet or phone. The victims of social engineering could be the organization’s employees, or any other authorized entity present from the organization’s network.
- Physical: It is used to test applications installed at the client site.
- Remote test: Testing the modem or similar object may provide access to connected systems and servers.
Penetration Testing Techniques
| Manual Penetration Test Experts in this field find vulnerabilities and risks through a manual scan. In a manual test case, an engineer performs the task and uses various tools for testing. |
| Automated Penetration Test This test is efficient and faster compared to manual testing since a machine automatically checks for vulnerabilities and risks. No engineer is required; it can be performed by anyone, even if they have less knowledge about the field. Popular tools for automated penetration tests are Nessus, Metasploit, OpenVAS, backtrack, etc. |
Penetration Testing Vs. Vulnerability Assessment
While the objective of a pen test and vulnerability assessment is to identify security flaws in networks and systems, there are key differences between them:
Penetration Test |
Vulnerability Assessment |
| A pen test is a manual process where a consultant conducts an assessment on a target to reveal the vulnerabilities by exploiting them. | In this process, threats and vulnerabilities are identified on a target using automated vulnerability scanners. |
| The primary goal is to gain unauthorized access through exploitation, which can be used to emulate a malicious hacker’s intent. | In rare cases, manual testing is conducted with additional tools to evaluate the security of applications. |
How Is Penetration Testing Done?
Stages of Pen Testing
This section dives deep into the different stages of pen testing and how an organization can benefit by regularly conducting these tests and keeping their IT domain protected and secure.
1. Planning
The first phase comprises of the planning stage. Here, all the goals and objectives of the pen testing are defined. To maintain consistency throughout the testing process, both the client and the pen tester define the objectives. The common purpose is to:
- increase and improve the security of the organizational IT infrastructure.
2. Reconnaissance
In this phase, to move further with the testing process, the pen tester requires detailed information about the systems and network. This phase consists of the preliminary information analysis such as IP address, social engineering, domain name searches/WHOIS lookups, mail addresses, usernames, dumpster diving, etc. The pen tester gathers as much information on an organization’s weak aspects and the potential targets for exploitation.
3. Discovery
In this step, a penetration tester uses automated tools to scan target assets for discovering vulnerabilities. These tools typically have their databases providing details of the latest vulnerabilities. The tester discovers:
- Network discovery: Includes the discovery of new systems, servers, and other devices.
- Host discovery: It determines open ports on these devices.
- Service interrogation: It interrogates ports to discover actual services that are running on them.
4. Analyzing information and risks
During the analyzing phase, the tester considers the following elements –
- The goal of the penetration test.
- Risks in the existing system.
- The estimated time required for evaluating the security flaws and start the penetration testing process.
However, from the list of identified systems, the tester test only those which contain potential vulnerabilities.
5. Active intrusion attempts
This is the most critical step in the pen test stage, and it must be performed with the utmost care. Since it entails the potential cyber vulnerabilities identified, that possess the risks, this step must be presented when verification of potential vulnerabilities is needed. For those systems with very high integrity requirements, the potential vulnerability and risk need to be carefully considered before conducting critical clean-up procedures.
6. Final analysis
The final analysis is the stage where the pen tester mentions all the steps performed, followed by the evaluation of each risk present in the system. The tester must ensure that the tests’ transparency is maintained, and the vulnerabilities are disclosed to the team.
7. Reporting
The final phase is the reporting stage. The report includes details comprising the overall testing procedure conducted, analysis of the vulnerabilities and the risks involved. The report must contain the findings and detailed explanations. This will help an organization gain insights and opportunities to improve their security posture significantly. The report should portray exactly how entry points were discovered and how you can remediate the security issues found.
The report must comprise the following sections.
- Summary of penetration testing.
- Details of each step and the information gathered during the pen-testing.
- Details of all the vulnerabilities and risks discovered.
- Details of cleaning and fixing the systems.
- Recommendations and implementations for future security.
5 Major Benefits of
Penetration Testing
An essential practice that each organization must follow is to perform regular penetration testing of its security posture. A periodic security check, penetration tests find the gaps in security before a hacker does by exploiting vulnerabilities and providing steps for remediation.
1. Identify risks
Performing regular pen tests allows an organization to gauge what security controls are required to maintain the protection of its people and assets. Once risks are identified, the firm can prioritize and prevent malicious attacks from happening.
2. Prevent hackers from infiltrating systems
Proactively performing regular penetration tests helps an organization to evaluate its IT infrastructure security. They will not only help uncover the pitfalls of your security system but will also give a chance to effectively remediate any shortcomings before an actual attack occurs.
3. Mature your IT environment
Upgrading the security posture of your organization’s IT environment is the key to maintaining maturity levels and staying competitive against other organizations in your industry. If an organization continues to stay abreast of security standards and compliance, your clients can see that you are continuously dedicated to striving towards optimum security.
4. Costly data breaches
One of the leading causes of concern for most IT firms is recovering from heavy losses because of a regular data breach within the industry. Periodic penetration tests are one way to keep your security systems secured as well as maintain security guidelines and procedures that will help prevent the financial loss of a breach, while also protecting your brand and reputation.
5. Comply with industry standards and regulations
Lastly, pen tests help address the compliance and security obligations that are mandated by industry standards and regulations. Having the tests performed regularly helps demonstrate due diligence, avoiding the heavy fines that can be associated with being non-compliant.
Areas of Penetration Testing
Penetration testing is typically done in the following three areas:
1. Network Penetration Testing
The aim of this testing is that the physical structure of a system such as workstations and servers are tested to identify the vulnerability and risk associated with it — tester identities, security flaws in the design, implementation, or operation of an organization’s system. The devices tested can be computers, modems, or even remote access devices.
2. Application Penetration Testing
The aim is to identify security issues resulting from insecure development practices in the design, coding, and publishing of the software. It exploits the efficiency of an application’s security controls by gauging vulnerability and risk.
3. Wireless Penetration Testing
The aim of this test is to focus on information security measures placed in Wi-Fi networks, analyzing the weaknesses, technical flaws, and critical wireless vulnerabilities present.
Penetration Testing Tools and Technologies
Penetration testing tools exploit the vulnerabilities within the network, using specific tools to identify gaps and misconfiguration. The best way to perform penetration testing is to conduct a series of regular and repeatable tests and to work through all the different application vulnerabilities.
What are the best penetration testing tools?
Below are the 6 best pen testing tools:
Metasploit
It is the most widely used pen testing tool. It is useful for checking security and identifying flaws and setting up a defense.
Nmap
This is a port scanner. It scans the systems and networks for vulnerabilities that are linked to open ports.
John the Ripper
Pen testers use this tool to launch attacks to crack a password weakness in systems or databases.
Nessus
This application scans open ports, weak passwords, and misconfiguration errors. Usually, Nessus is used for scanning IP addresses and websites.
Wireshark
This tool is a network analyzer/network sniffer/network protocol analyzer that assesses network traffic vulnerabilities at different levels.
Penetration Testing Process
- Pen test services go beyond technical vulnerability assessments. Inspecting the configurations of existing applications, operating systems, servers, firewalls, and other components are vital aspects of protecting against threats.
- Consequent to the completion of the penetration testing process, professionals conclude the results in a comprehensive report. The report comprises tools and techniques used while uncovering the weak points of your applications.
- The testing process ensures that the proposed implementations met are at par with compliance, standard guidelines, and frameworks.
Penetration Testing Approach
- A broad range of vulnerability scans and simulated attacks are performed using various methodologies and tools. To ensure the tests are conducted without affecting the business continuity and within the agreed timeline and scope, all the tests are as per the policy and service agreement.
- The most vital part of any analysis or test is the documentation. So, ensure these attacks, applications, and potential weaknesses are documented.
- The key to an efficient pen testing is to have the best security personnel who can design a comprehensive plan, from implementation to remediation.
- Determine and scan the systems, network components, and wireless connection points
5 Reasons Why You Need a
Pen Test in Your Organization
Stay abreast and one step ahead before an attacker spots the vulnerable areas of your system. Below are 5 reasons a pen test is a mandate for an organization:
| 1 | Distinguish the present security defense mechanism and assess if the systems are competent enough to handle any precipitate malicious attacks. |
| 2 | Periodic system upgrades ensure the avoidance of security flaws in the network. It is essential to frequently monitor the hardware, software, and applications of an organization. |
| 3 | Revise and restructure security policies, processes, and technologies to avoid and mitigate different business risks and issues. |
| 4 | Adhering to regulatory standards such as PCI-DSS, HIPAA, and GLBA avoids enormous fines for being non-compliant. |
| 5 | Penetration testing helps avoid costly security breaches that put your organization’s reputation and customers’ confidence at stake. |
Conclusion
Penetration testing helps to reduce the threats and risks that your business may face. If competent and robust, the security practices adopted can protect your business. A risk-based approach towards cybersecurity addresses the prioritized threats and reviews your business risk exposure continuously.
FAQs
Q: What is the role of a pen tester?
Pen testers are security specialists who attempt to breach computers and network security systems. They ensure that those without authorization cannot have access to an organization’s data. They hack into networks to identify potential vulnerabilities in the system. The aim is to automate the hacking process, but testers can also manually make attempts to breach security.
Read More: https://blog.eccouncil.org/5-penetration-testing-methodologies-and-standards-for-better-roi/
Q: What skills does a pen tester require?
A pen tester should have hacking experience and possess skills in advanced computer skills, scripting, programming, report writing, data analytics, and information security.
Read More: https://blog.eccouncil.org/advanced-penetration-testing-penetrating-the-most-advanced-networks/
Q: What are the types of pen testing?
The types of pen testing are network pen tests, wireless pen tests, and physical pen tests. The network pen test comprises of black, white, and grey box. Wireless consists of an application security pen test, while a physical pen test consists of remote and physical.
Read More:
