
How to Manage Event in SOC
What is SIEM and how does it work
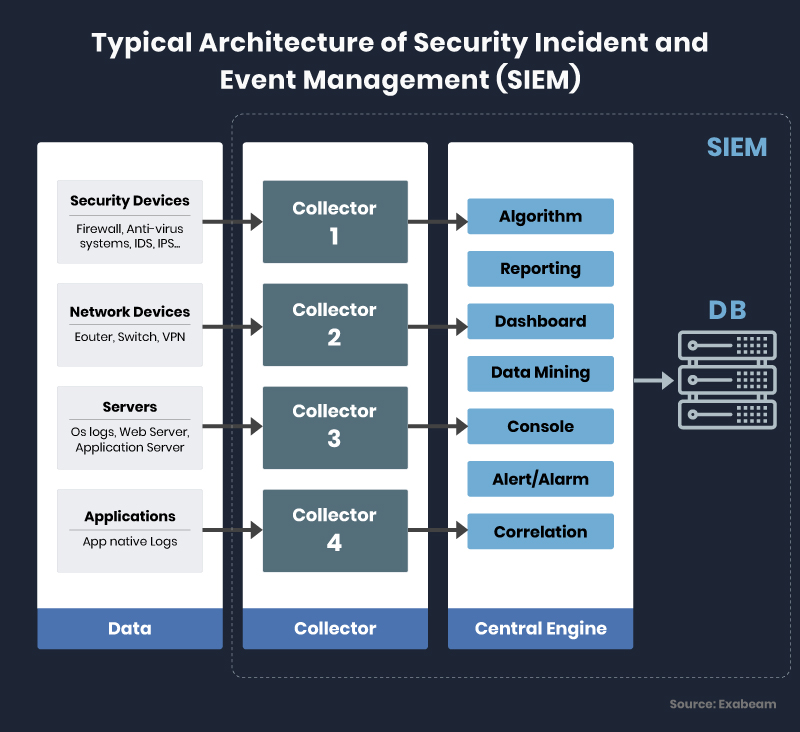
Security incidence and event management contribute to 1.6% of the total $120 billion economies of the cybersecurity industry. Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) is a software solution that collects and analyzes data from different sources and assets of an organization’s IT infrastructure to look for possible vulnerabilities. As SIEM tools collect data from network devices, servers, domain controllers, and more, they are an essential part of the data security environment. SIEM collects, stores, normalizes, aggregates, and applies analytics to that data to study the trend, and detect vulnerabilities to help organizations strengthen their security structure.
SIEM is generally used by the Incident Response team for creating an alert based on threat indicators that match certain criteria and to conduct and report forensics results of a security incident. SIEM is a data complier and reporting system that follows a predefined set of rules, the result of which is used by security engineers to study a breach. The major functionalities of SIEM are security monitoring, threat detection, forensics, incident response, log collection, normalization, notifications/alerts, incident detection, etc. some SIEM tools also provide incident management protocols and guidelines. Apart from its core function of data gathering and log management, SIEM application is also incorporated within the security structure to demonstrate compliance for regulations like HIPAA, PCI, SOX, and GDPR. SIEM tools can also help an organization to calculate their bandwidth, capacity, and data growth, upon which the stakeholders could make important investment and financial decisions. Some of the popular SIEM tools are listed below for reference.
SIEM tools
- Splunk: Splunk is one of the most renowned SIEM tools in the cybersecurity market. It features security monitoring along with an advanced threat detection module.
- IBM QRadar: QRadar is another popular SIEM virtual application that can be incorporated as a hardware application or software application based on the requirement and capacity of an organization.
- LogRhythm: Designed for smaller organizations, LogRhytm can be integrated LogRhythm with SIEM guidelines to generate advanced detection features.
- SolarWinds: SoalrWind is easy to deploy, cost-effective, and supportive; it is much more suitable for organizations with limited security features.
- Sumo Logic: Sumo Logic is relatively new and offers solutions for cloud, hybrid, and DevSecOps environments.
Limitations of SIEM applications
SIEM applications are only effective as its source data. Without any additional context on that data, SIEM often results in false alarms or insignificant issues. The greater amount of low-level data leads to a high number of alerts, thus proving it difficult to locate the actual malicious activity.
SOC (Security Operations Center)
Security Operations Center (SOC) is the process/department that handles threat incidence. It could be an in-house department or a third-party vendor that handles IT incidents on behalf of an organization using people, processes, and technologies that help provide threat awareness and remediation with the help of detection tools. Its core role is to ensure the proper identification of threats through indicator analysis, communication, investigation, and reporting. The SOC also monitors intrusion detection tools for probable unauthorized access or cyberattack onto the network through determining the authenticity of threat indicators and the scope of its damage to the business process. The establishment of a Security Operations Center requires huge operation costs and valid reasons such as protecting the high level of sensitive information. It also compliance such as PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) and CESG GPG53 (Communications-Electronics Security Group Good Practice Guidelines).
SOC is typically based around security information, and event management (SIEM) system which provides the proceed data from its feeds of threat indicators such as:
- Network discovery and behavior analysis
- Penetration tests
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS)
- Intrusion Prevention System (IPS)
- Web site assessment systems
- Application scanner
- Vulnerability assessment
- Risk and compliance systems
- Database scanners
- Log management systems
- Cyber threat intelligence
- Firewalls
- Antivirus
- Unified Threat Management (UTM).
These data outputs of SIEM now acts as input for SOC team, which consist of certified security engineers such as, SOC analyst (CSA), Security Analyst, Network Defender (CND), CCISO (Chief Information Security Officer), etc. who plan and test all the possible scenarios for a probable incident occurrence, and its mitigation.
Generally, large organizations and governments tend to operate SOC, and sometimes more than one to either, help manage different sets of information or to act as a backup in case of failure or unavailability of one. Security Operations Centers’ role can also be outsourced to third-party specialists, also known as managed security service. This is generally done by smaller organizations as setting up an inhouse SOC facility is costly. The Security Operations Center and the Network Operations Center (NOC) often augment each to produce a more dependable collaborated result. Where the NOC is responsible for maintaining and assessing the overall network infrastructure for vulnerabilities, the SOC is responsible for protecting other cybersecurity infrastructure assets such as web applications, databases, servers, data centers, etc. Similarly, SOC and physical security operations center which monitors people and endpoint tools such as security officers/guards, alarms, CCTV, physical access, etc.
Functionality
The methodology of SOC is laid out through guidelines and protocols that define responsibilities, technologies, business processes, operations, and analytical procedures. These predefined steps help the security engineers in the event of an alert or breach to process escalations, reporting, response, and mitigation. The latest trends in Security Operations Center have extended into cloud computing and the advanced technology incorporation.
CloudSOC: A cloud security operations center (CloudSOC) is set up to monitor cloud service which hosts colossal amount of data and have a greater probability of breach incident. This process is majorly carried out by third-party vendors as cloud solutions are always outsourced. The major benefit of CloudSOC is ample availability of SIEM data, as cloud host information from multiple organizations, all their indicators, or SIEM results in the cloud, could be used by CloudSOC to yield better results.
SmartSOC: A Smart SOC (Security Operations Center) is a comprehensive solution involving the use of cutting-edge technology and tools, highly skilled and experienced cybersecurity experts. This is based on proactive cyber warfare principles, that aims to prevent and neutralize threats against an organization’s digital infrastructure, assets, and data.
Augmenting SIEM and SOC with EGS
As described above, Organizations are continuously expanding their operations, leading to a vast and complex system of applications and colossal amounts of data. These developments, along with increasing financial gains, also increases the risk and vulnerabilities which could be exploited by the threat actors. Also, the increasing regulatory pressures, compel an organization to incorporate Security Incident and Event Management (SIEM), and Security Operation Center (SOC) as comprehensive measures of security. But, for smaller organizations incorporating these measures by themselves will cost a lot of money. Thus, utilizing EGS solutions for SIEM and SOC outsourcing will help organizations save a substantial amount of money.
EGS Approach:
EGS (EC-Council Global Service) works with your IT security assets to generate and assess a Security Information & Event Management (SIEM) solution and operational security to mitigate probable risk to your business process. EGS’s unique approach leverages the general and specialized protocols, guideline, and cybersecurity knowledge to consider:
- Use of information – Information is required for SIEM tools and efficient aggregation towards threat analysis and demonstration towards compliance with regulatory requirements in the industry. When considering data protection, EGS guidelines layout standard protocols to ensure the acquisition of enough promising data for analysis and reporting.
- Proactive approach – Analyzing the probability of possible threats facing your organization towards its occurrence, threat detection via indicator analysis, and its mitigation. Preparation towards future incidents via scanning and analysis of vulnerabilities and its probable exploit curve to proactively protect your organization from future threats.
- Layered security – Projecting the importance of event monitoring and its augmentation to an organization’s layered security approach in prioritizing security incidents.
- Effective model – Helping to determine the model of operational security effective to an organization’s business needs. Formalizing effective protocols for responsibilities, monitoring, incident investigation, mitigation, and response activity.
- Increased efficiency – Leveraging contextual information for manual compliance activities, and its automation for increasing the efficiency of an organization’s security operation.
FAQs




